Aim¶
To show the interference of two coherent beams of light.
Subjects¶
6D10 (Interference From Two Sources)
Diagram¶
Diagram
Equipment¶
Laser
Simple lens (we use )
Surface mirror
White screen/wall
Presentation¶
The room is darkened and the laser is switched on. By means of the -lens an illuminated disk is projected on the white screen. The surface mirror is placed parallel to the diverging light beam (see Figure 1A)

and then turned just a little, so that the outer rays of the beam are reflected (see Figure 1B). In the light spot on the wall the fringes are visible now.
Explanation¶
A portion of the wavefront is reflected from S (see Figure 2).
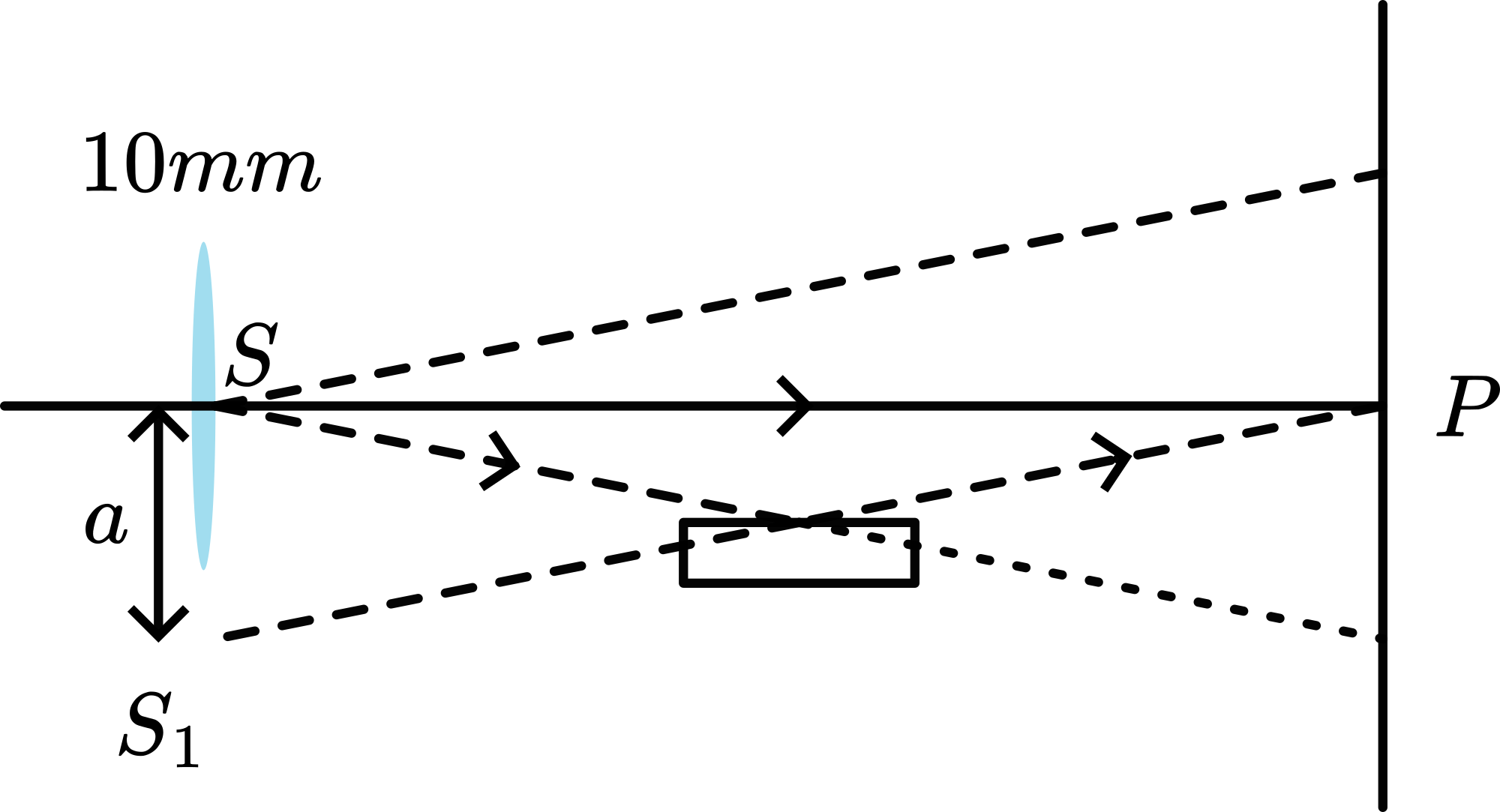
The other portion proceeds directly to the screen. Interference occurs in the region where the two portions are superimposed and its mirrorimage can be considered as separate coherent sources, placed a distance apart. Then the separation ( ) between the fringes is given by ( being the distance between the plane of the two sources and the screen).
Remarks¶
In the demonstration the distance between the fringes can be enlarged by placing the screen not perpendicular but more parallel to the beam.
Sources¶
Hecht, Eugene, Optics, pag. 391-392
Leybold-Heraeus, Physikalische Handblätter, pag. DK 535.412;b