08 Precession (3a)#
Aim#
To show how a rotating wheel reacts to an applied torque.
Subjects#
1Q50 (Gyros)
Diagram#
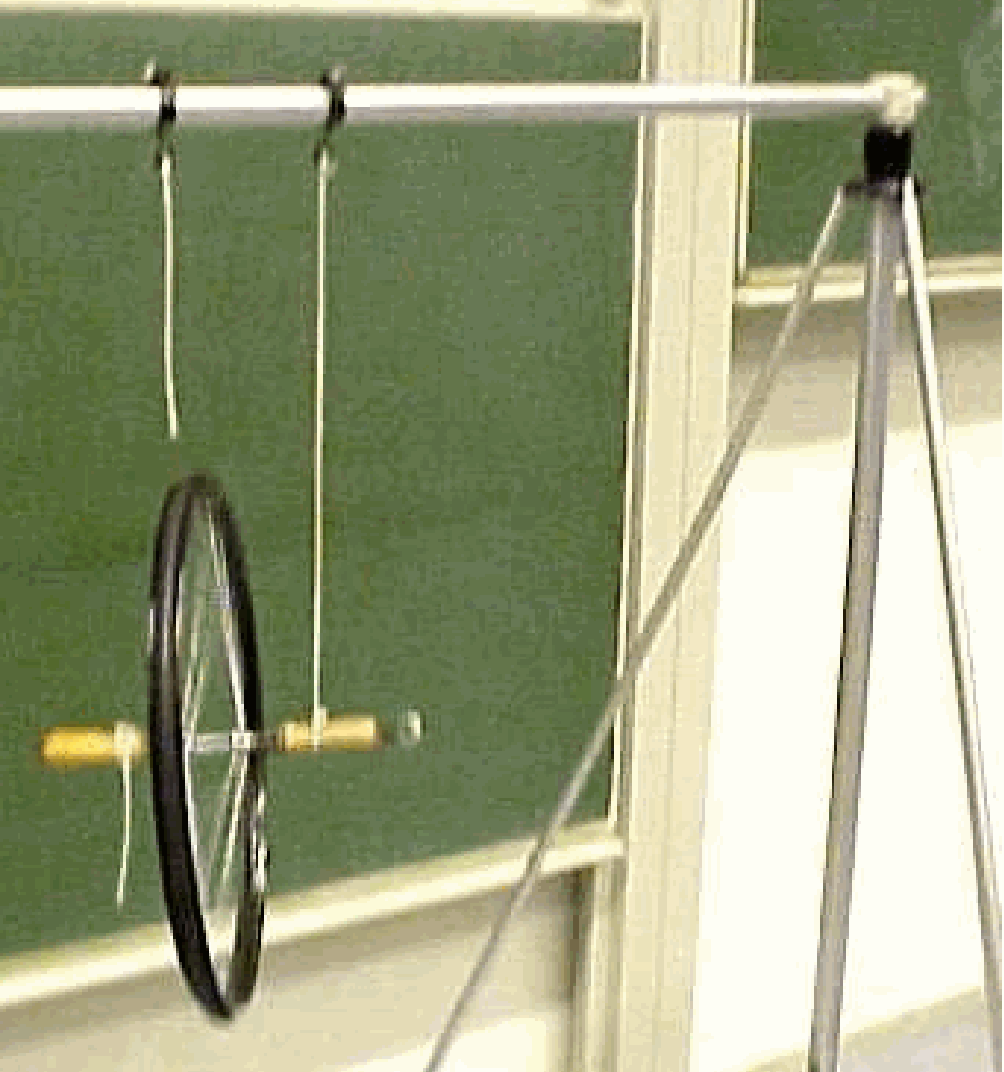
Fig. 258 .#
Equipment#
bicycle wheel with handles
1 piece of rope
1 stick
Presentation#
The wheel is rotating and held by a string. The rotating wheel has an angle of about \(45^{\circ}-60^{\circ}\) with the vertical. The wheel will precess about a vertical axis. When the instructor pushes with the side of his hands or a stick against one of the handles of the wheel in the direction of precession, then the rotating wheel will rise to a more vertical position. This can be continued, even passing the vertical.
Explanation#
The rotating wheel will precess due to gravitational torque, \(m g s\) ( \(I \omega_{0}\) moves in the direction of this gravitational torque; precession) (see Figure 259a).
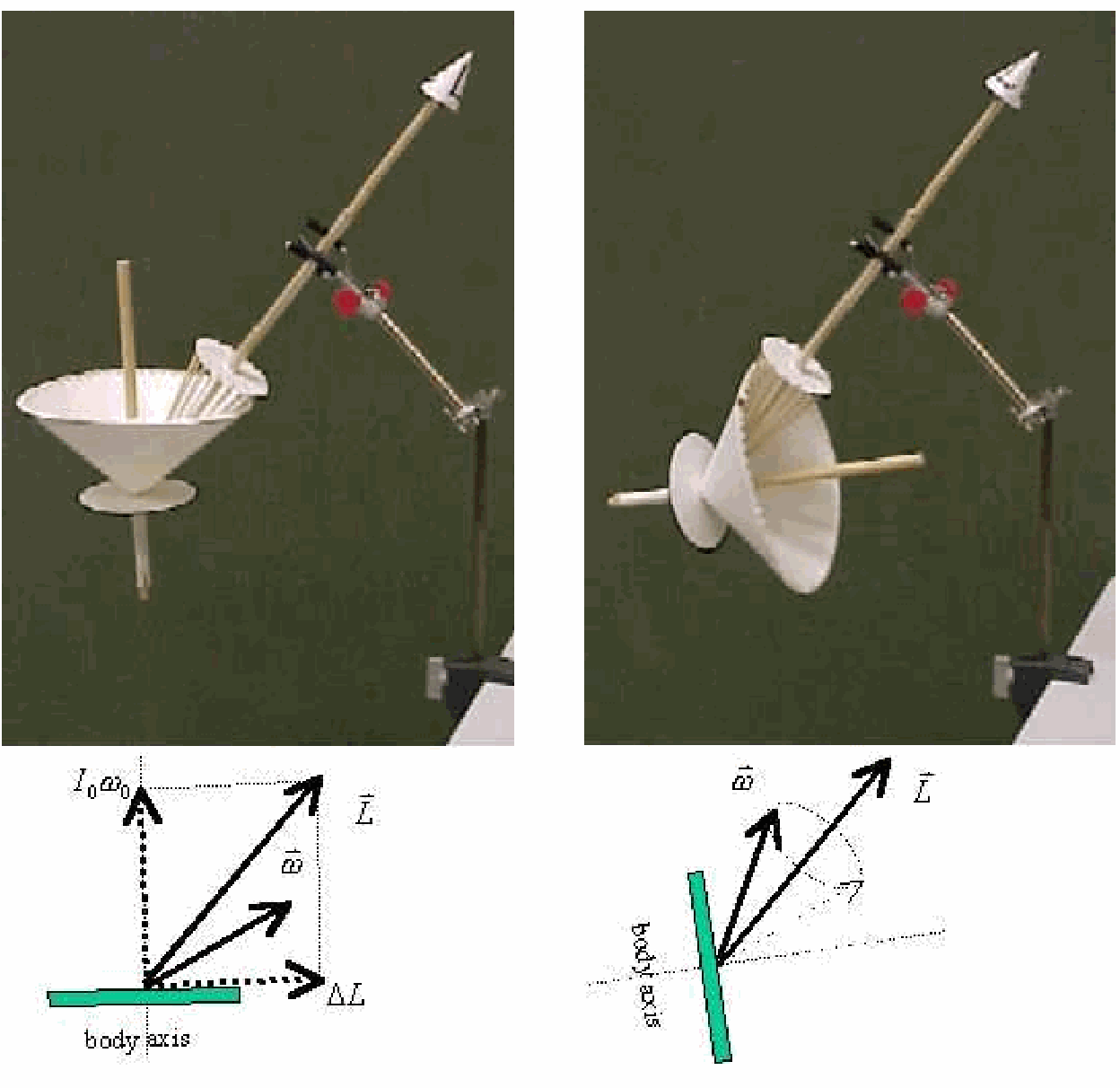
Fig. 259 .#
\(F\) is the applied force in the direction of precession (see Figure 259b). The applied torque is pointing vertically upward, so now \(I \omega_{0}\) moves also upward.
Video Rhett Allain#
Sources#
Freier, George D. and Anderson, Frances J., A demonstration handbook for physics, pag. M-53
Sutton, Richard Manliffe, Demonstration experiments in Physics, pag. 79
