02 Handheld Standing Waves#
Aim#
To show the normal modes of a standing wave on a string (nodes and antinodes).
Subjects#
3B22 (Standing Waves)
Diagram#

Fig. 349 .#
Equipment#
Standing-wave generator
White string
Black screen
Small clamp
Presentation#
The white string is fixed to the standing-wave generator (see the first topic in “Remarks” for a description of the standing-wave generator). Hold the standing-wave generator by the string close to the device.Slowly increase the amount of string by which the generator is suspended and you will see standing waves at specific lengths of the string(see Figure 350).
Explanation#
The fundamental frequency of a vibrating string fixed at both ends is \(f=n\left(\frac{1}{2 l}\right) \sqrt{\frac{T}{\mu}}\).
\(T\) (the tension in the string) and \(\mu\) are constant in this demonstration ( \(\mu\) is the mass per unit length of the string). So at a certain length \(l\), we observe the first normal mode \((n=1)\).
Doubling the length reduces the fundamental frequency of the string by a factor 2 . Since \(f_{\text {qenerator }}\) is constant we observe now the normal mode of the second harmonic (first overtone; \(n=2\) ) of that fundamental frequency. And so on.
Remarks#
To make the generator vibrate, a dowel is fixed eccentrically to the shaft of the motor. We obtain lower frequencies by clipping a small clamp to the dowel (see Diagram). Shifting the clamp changes the frequency.
Be sure that the clamp is fixed strong enough so it will not fly away when the device is vibrating.
In order not become entangled in the string while demonstrating, the free end of the string hangs down across the shoulder of the demonstrator (see Figure 350)
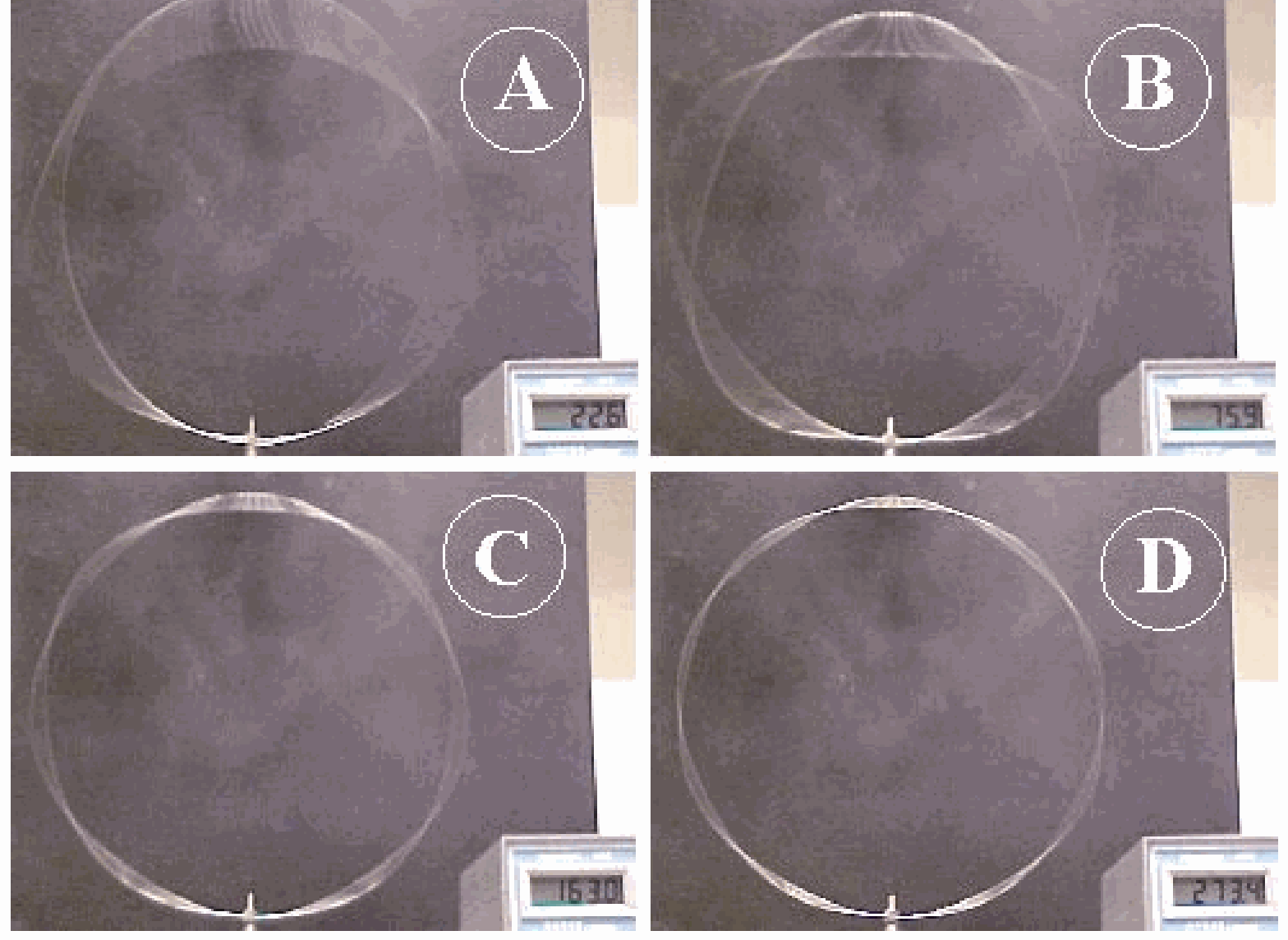
Fig. 350 .#
Sources#
Mansfield, M and O’Sullivan, C., Understanding physics, pag. 336-338 and 344-345
Young, H.D. and Freeman, R.A., University Physics, pag. 627-629
The Physics Teacher, Vol. 38 sept. 2000
