01 Boiling to Freeze#
Aim#
To show that boiling evaporation requires a lot of heat.
Subjects#
4C30 (Phase Changes: Liquid-Gas)
Diagram#

Fig. 406 .#
Equipment#
Vacuum pump
PVC-cylinder with transparent end caps and a small table inside.
Dripper.
Camera and projector focused on the drop of water.
Safety#
In using the vacuum pump, never expose parts of the body to the created vacuum. There is a danger of injury. Never operate the pump with an open, and thus accessible, inlet. Do not open the vacuum system during operation of the pump.
Presentation#
Preparation#
The vacuum pump is connected to the cylinder. One rim of the cylinder is greased with vacuum grease, and then one of the square transparent end caps is pressed to the cylinder, creating the bottom of the assembly. The upper rim of the cylinder is also greased, after which the small table is placed inside the cylinder.
Fig. 407 .#
Preparation#
Using a dripper, a large drop of water is deposited on the tabletop. The second transparent end cap is put on top of the cylinder and pressed down. The assembly is ready now (see Figure 407) and the camera is focused on the drop of water.
The pump is switched on, after which vigorous boiling can be immediately observed.
This stops, and a quiet drop of water is observed.
Then, after some time, suddenly the drop of water turns opaque (see Figure 408)
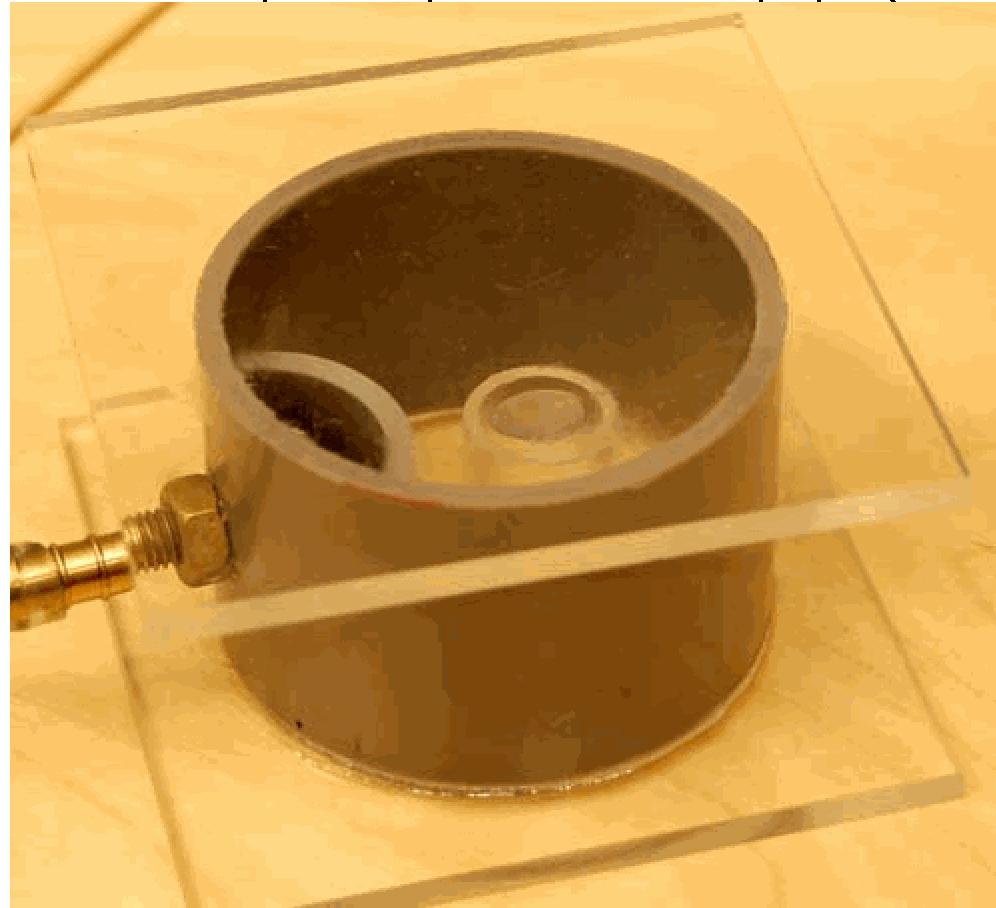

Fig. 408 .#
We stop the pump, remove the upper transparent cap, and shift the frozen drop across the table using a small stick. This shows the audience that the drop is solid.
Explanation#
When the pump is switched on, the water starts boiling due to the low pressure. This boiling is vigorous due to the fast drop in pressure.
Then, after some time, this boiling stops because the decrease in pressure is now continuing at a slower rate. (The evaporation of water continues in this part of the demonstration but is not visible to us now.)
During the process of boiling and evaporation, the drop of water loses heat and its temperature decreases. Because the small tabletop is very clean, the drop of water even becomes supercooled; it reaches a temperature below its freezing point of \(0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), at which it suddenly freezes.
Video Rhett Allain#
To further showcase the boiling of water at reduced pressure.
