03 Physical Pendulum (3) Oscillating Ring#
Aim#
To show a particular example of a compound pendulum.
Subjects#
3A15 (Physical Pendula)
Diagram#
Fig. 308 .#
Equipment#
2 large (steel) rings, \(\varphi=600\) with knife-edge suspension. Th ese rings can be divided into \(2 / 3\) and \(1 / 3\).
mathematical pendulum, \(\mathrm{I}=600\)
meterstick
Presentation#
One complete ring swings in its plane at the knife-edge on its periphery. A simple pendulum whose length is equal to the diameter of the ring is suspended beside it so the equality of periods can be observed.
A second \(2 / 3\)-ring is made swinging. It can be observed that the ring has still the same period!
Again the same period is measured when \(1 / 3\)-ring is swinging
Explanation#
For a physical pendulum, the period \(T\) is given by \(T=\frac{2 \pi}{\sqrt{g}} \sqrt{\frac{I_{A}}{m s}}\).
If the pendulum is a complete ring, then \(s=R\) (see Figure 309), \(I_{A}=I_{C}+m R^{2}\) and \(I_{c}=m R^{2}\). Then \(T=\frac{2 \pi}{\sqrt{g}} \sqrt{2 R}\), so \(I_{r}=2 R\).
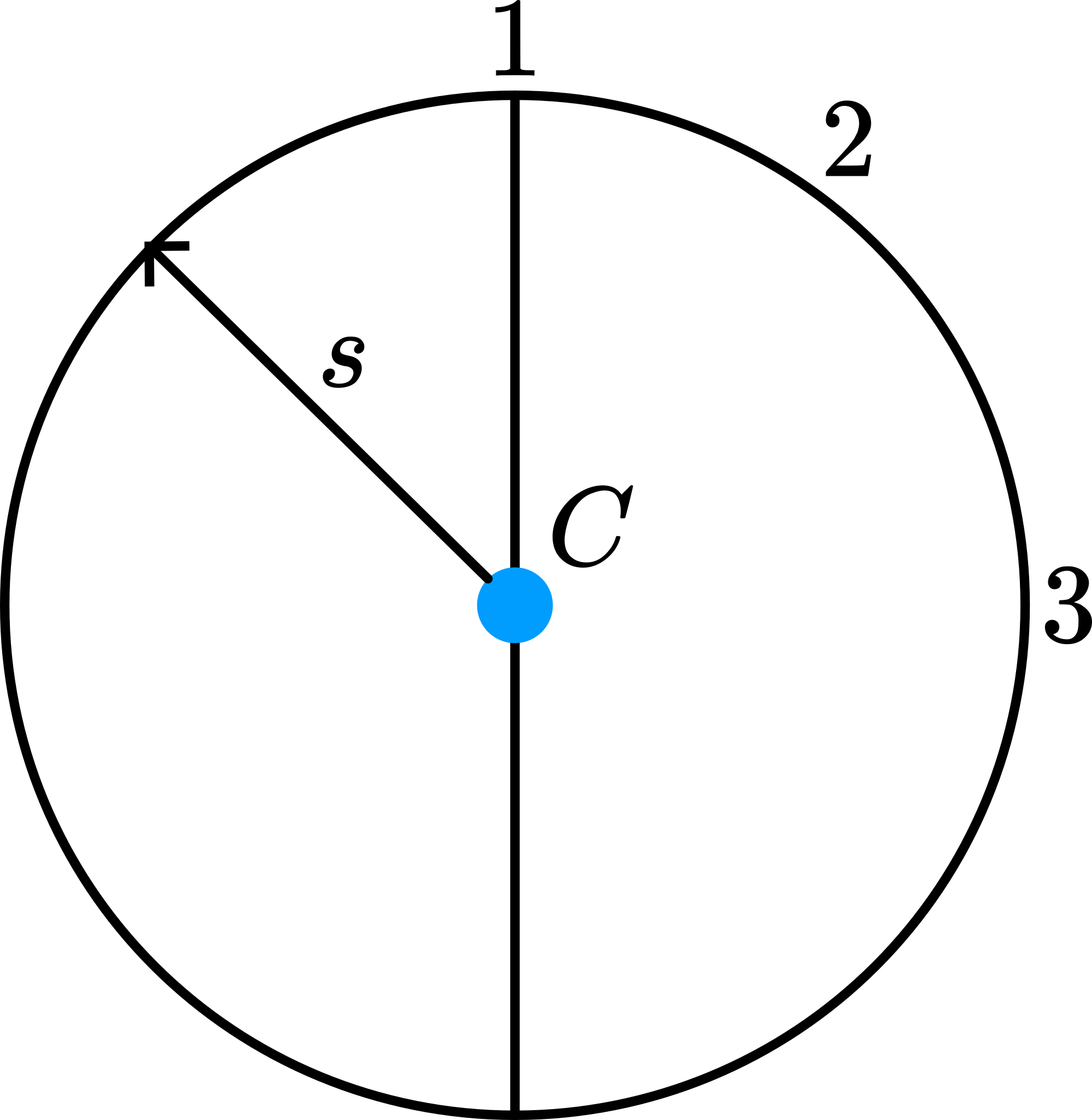
Fig. 309 .#
So a complete ring has the same period as a mathematical pendulum of length 2R.
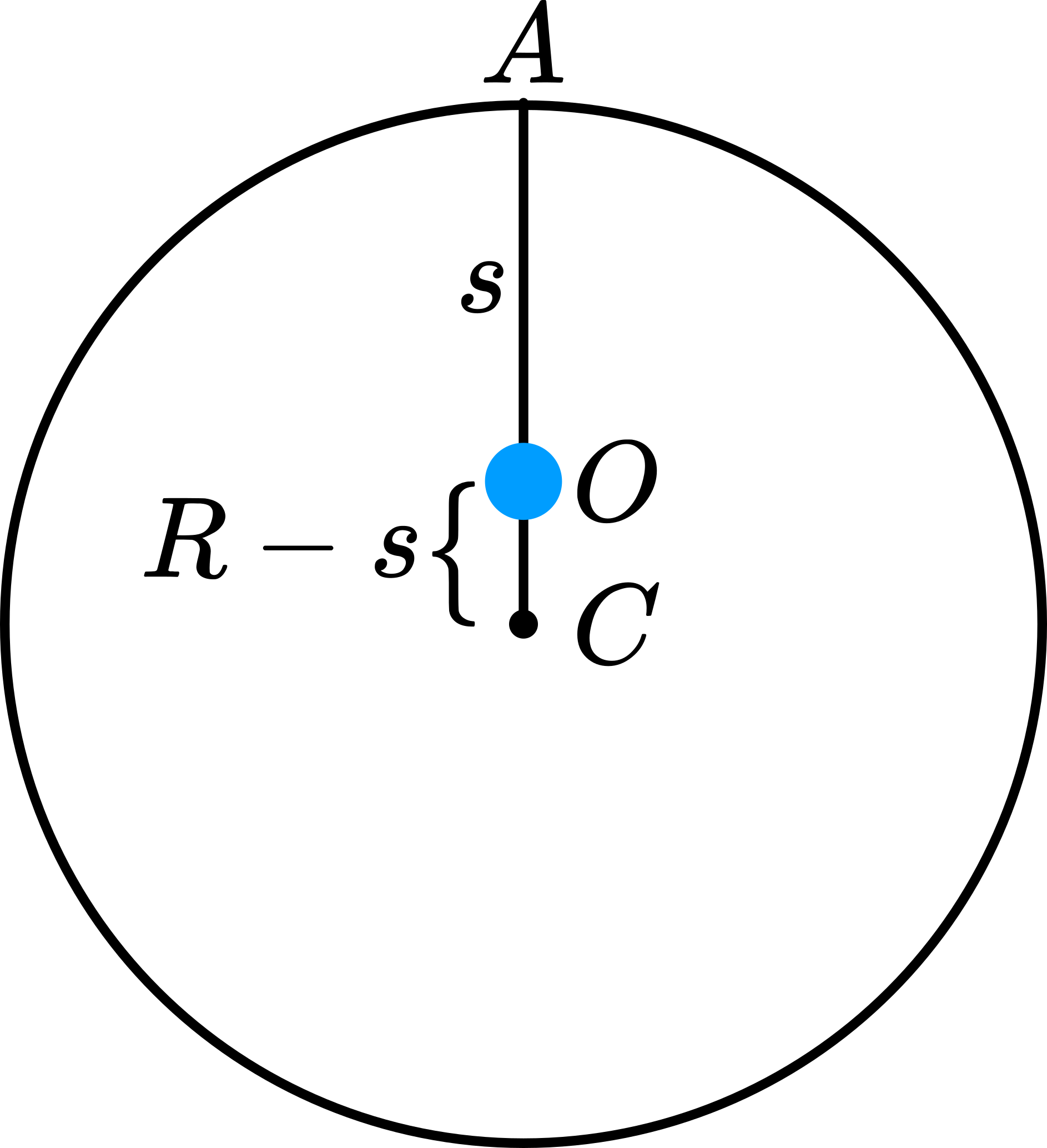
Fig. 310 .#
If the pendulum is part of a complete ring, \(I_{O}=m R^{2}\) (Figure 310). Also \(I_{O}=I_{C}+m(R-\) \(s)^{2}\) (C is the center of mass) and \(I_{A}=I_{C}+m s^{2}\). It follows that \(I_{A}=2 m R s\) and \(T=\frac{2 \pi}{\sqrt{g}} \sqrt{2 R}\). So again \(I_{r}=2 R\).
Sources#
Ehrlich, R., Why Toast Lands Jelly-Side Down: Zen and the Art of Physics Demonstrations, pag. 126-127
Roest, R., Inleiding Mechanica, pag. 169-170
Sutton, Richard Manliffe, Demonstration experiments in Physics, pag. 88
